Madrileña Red de Gas continues to invest in and advance the possibility of using its existing gas infrastructure to decarbonise the gas sector. This is an
important step towards achieving the country’s carbon emission reduction targets; the company is aware that the combination of biomethane and renewable hydrogen can provide effective and sustainable solutions for the transition to cleaner and more environmentally friendly energy.
In this regard, during 2023, Madrileña Red de Gas participated in and developed a range of green projects, such as the installation of a 100% hydrogen boiler at its facilities and the Inspira Madrid and Pryconsa projects.
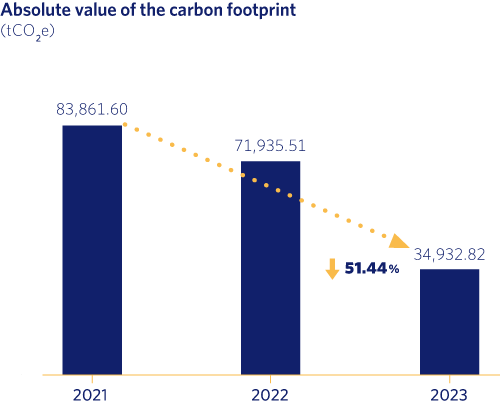
In relation to the company’s commitment to the fight against climate change and to reducing emissions, the most important milestones in 2023 were the adherence to the OGMP 2.0 initiative: the Oil & Gas Methane Partnership 2.0 of the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) for the reduction of methane emissions and the reduction of the carbon footprint by more than 51%.
5.1 NGV (natural gas vehicle)
The price of natural gas stabilised over the course of 2023, making it the most competitive fuel in the mobility sector. There are only a few passenger car models on the market, but due to their economy and low emissions, NGVs have established themselves as the fuel of choice for transport professionals, a sector in which there is a wider choice of vehicles, and conversion to NGVs is also possible.
NGVs provide access to the low-emission zones that municipalities with more than 50,000 inhabitants will be obliged to activate in the coming years, and guarantee the necessary autonomy.
NGVs provide access to the low-emission zones that municipalities with more than 50,000 inhabitants will be obliged to activate in the coming years, and guarantee the necessary autonomy.
It should also be noted that refuelling time is the same as for conventionally fuelled vehicles. The fleet of natural gas vehicles now exceeds 35,000; the biggest increase has been in truck registrations, more specifically those of compressed natural gas (CNG), which grown by 51% in 2023 compared with the previous year.
Madrid is the Autonomous Community with the largest NGV fleet, due largely due to the existing network of gas stations, which facilitates the use of this fully functional, accessible and economical alternative fuel
It is known and proven that NGVs are currently one of the most economical transport alternatives, without increasing the cost of vehicle purchase.
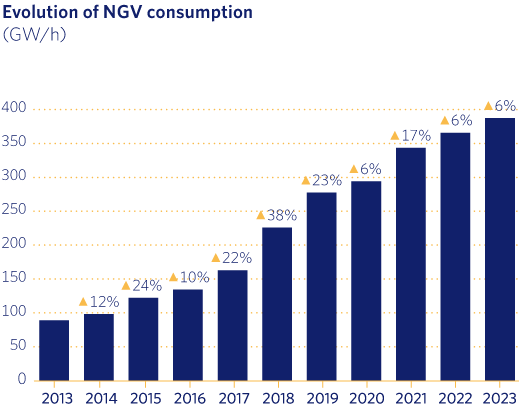
NGV consumption in Madrileña Red de Gas continued to grow over the course of 2023, reaching 365 GW/h. The cumulative increase over the past five years is around 58%.
Currently, there are 20 NGV stations connected to the Madrileña Red de Gas networks, of which 11 are public access stations. They are located in the capital and in the most populated municipalities in the south of Madrid, where the most important industrial estates in the region are concentrated. This ECO-labelled fuel can be refuelled there.
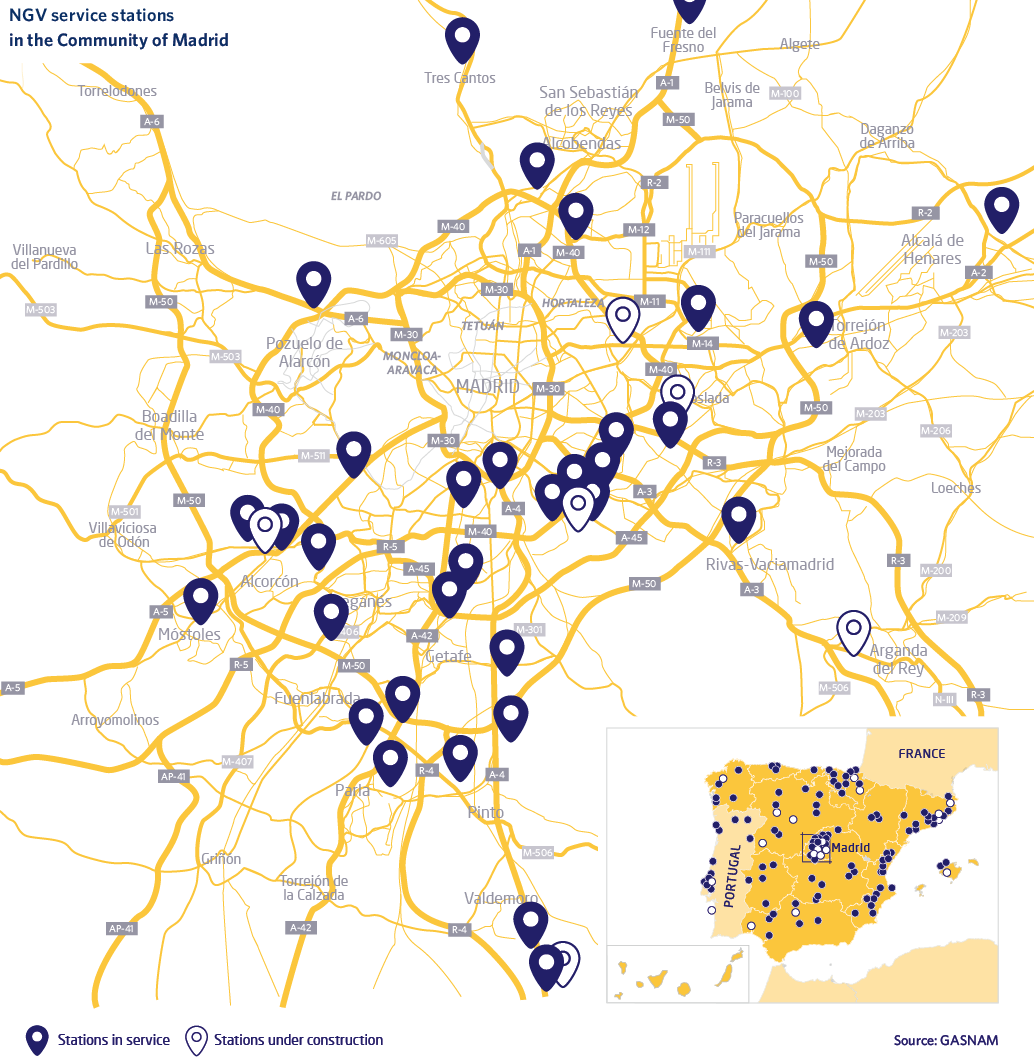
Madrid is the Autonomous Community with the largest NGV fleet, due largely due to the existing network of gas stations, which facilitates the use of this fully functional, accessible and economical alternative fuel.
To conclude, and by way of emphasising the benefits of the use of natural gas in mobility, the system of guarantees of origin for biomethane has been in operation since the second quarter of 2023. This allows any consumer to choose green gas from renewable sources. It is therefore entirely feasible, and in fact is already happening, for NGVs to run on biomethane, reducing their emissions to zero. Although not ratified by the system of guarantees of origin, it became a reality in 2021.
In 2023, 16.05 GW/h of biomethane was consumed in road transport. There are 12 biomethane plants operating on the Iberian Peninsula and almost a hundred plants under construction and in the pipeline, which have injected 244 GW/h of biomethane into natural gas infrastructures.
5.2 Environment
Throughout the year, the main focus of environmental performance was on maintaining the processes that underpin the integrated environmental management system, which has enabled Madrileña Red de Gas to maintain its certification in accordance with the ISO 14001:2015 standard.
As a result, Madrileña Red de Gas succeeded in reducing its total carbon footprint by more than 51% compared with the previous year, making a significant contribution to the achievement of the “Fit for 55” targets for 2030 and to “Net Zero” for 2050
Once again, the carbon footprint associated with the company’s activities was calculated and verified according to the ISO 14064 standard, including direct greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (scope 1), indirect GHG emissions from the generation of electricity purchased and consumed (scope 2), and indirect emissions occurring in the value chain (scope 3).
As a result, Madrileña Red de Gas succeeded in reducing its total carbon footprint by more than 51% compared with the previous year, making a significant contribution to the achievement of the “Fit for 55” targets for 2030 and to “Net Zero” for 2050.
As in previous years, how compliance with the requirements of environmental legislation is identified and assessed was managed using a specific application, and the notification of contaminated soil reports from decommissioned LPG plants continued at a good pace.
Madrileña de Gas also continues to reinforce its commitment to the circular economy, guaranteeing the correct management of waste within the framework of its integrated environmental management system, and applying techniques and alternatives that prevent and reduce the generation of waste at source, as well as the recovery (reuse or recycling) of this waste.
OGMP 2.0 adherence
One of the key environmental milestones in 2023 was the company’s adherence to the OGMP 2.0 initiative: the Oil & Gas Methane Partnership 2.0 of the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
In its fight against climate change, Madrileña Red de Gas is applying specific measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and help to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
Specifically, this initiative will create a new global standard for measuring methane emissions, in order to facilitate how they are monitored and establish plans to reduce them, guaranteeing transparency. The project, which is part of the EU strategy to reduce methane emissions, will apply to the entire value chain of the oil and gas industry, including production, transport and processing.
OGMP 2.0 will also serve as a framework for the European Commission to develop a legislative proposal on the mandatory measurement, reporting and verification of all methane emissions from the energy sector.
In its fight against climate change, Madrileña Red de Gas is applying specific measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and help to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
To date, 127 companies with assets on five continents, representing 37% of global oil and gas production, have joined the alliance. OGMP 2.0 is the reference standard from which the accuracy and transparency of methane emissions reporting in the oil and gas sector will be improved.
In this regard, Madrileña Red de Gas has an ambitious Action Plan that envisages the development of ten goals that will allow us to make progress and define the path to follow in terms of reducing methane emissions from our activities.
5.3 Inspira Madrid
Carried out in consortium with FRV and Grupo Ruiz, the Inspira Madrid project continued to be defined and make progress during 2023. Its objective is to participate in the hydrogen value chain, with the aim of decarbonising urban public mobility fleets in the Community of Madrid.
The first phase consists of constructing an electrolyser (in the northwest of Madrid), as well as five hydroline stations, located in different parts of the region. During the second phase, ten more hydroline stations are planned, which will be open to the public and offer a clean and sustainable fuel supply for vehicles with hydrogen technology.
The commitment of the three companies that include Inspira Madrid was strengthened in 2023 with the creation of the company Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) Inspira Madrid Hidrógeno Verde S.L., in which each partner has a 33.33% share.
CEF Transport European Programme
The CEF programme is a key EU funding instrument for the development of the European Green Pact and an important enabler of the EU’s decarbonisation objectives between 2030 and 2050
In 2023 Inspira Madrid was presented to the European aid programme Connecting Europe Facility (CEF) Transport.
The CEF programme is a key EU funding instrument for the development of the European Green Pact and an important enabler of the EU’s decarbonisation objectives between 2030 and 2050.
CEF Transport supports the development of high-performance, sustainable and efficiently interconnected trans-European networks in the fields of transport, energy and digital services. Investments in this programme complete the missing links in Europe’s energy, transport and digital backbone.
It also benefits the citizens of Member States by making travel easier and more sustainable, strengthening Europe’s energy security while allowing greater use of renewable energies and facilitating cross-border interaction between public administrations, businesses and citizens.
In addition to grants, the CEF offers financial support to individual projects through innovative instruments such as guarantees and bonds. These create a significant multiplier effect in their use of the EU budget and act as a catalyst to attract more funding from the private sector and other public sector actors.
CEF Transport is the financing instrument for the development of European transport infrastructure policy. It was created with the aim of supporting investment in the construction of new transport infrastructure in Europe and to rehabilitate and modernise existing infrastructure.
The goals of the Trans-European Transport Network Policy (TEN-T) envisage:
- By 2030: completion of the core network, structured around nine multimodal corridors.
- By 2050: completion of the comprehensive network, providing accessibility to all European regions.
The CEF initiative focuses on cross-border projects and projects aimed at removing bottlenecks or bridging missing links in various sections of the core network and the overall (feeder) network. It also deals with horizontal priorities such as traffic management systems.
The programme also supports innovation in the transport system in order to improve infrastructure use, reduce the environmental impact of transport, improve energy efficiency and increase safety. To this end, it has been endowed with a budget of €25.81 billion.
Hydrogen auctions
In turn, the project has been submitted to the first auction under the European Hydrogen Bank, with initial funding of €800 million from emissions trading.
This auction is aimed at supporting renewable hydrogen production in Europe by offering fixed premiums per kilogram of hydrogen produced to close the gap between the cost of production and the current market price.
The selected producers will receive subsidies and will be able to earn additional income from the sale of hydrogen on the market for up to 10 years. Any accumulation with other State aid is prohibited in order to ensure a level playing field between projects. In addition, an “auctions as a service” mechanism is introduced to finance additional projects.
A second round of auctions is planned for 2024, through which the European Hydrogen Bank plans to encourage renewable hydrogen production and imports, unlock private investment and address initial investment challenges in the EU and beyond.
5.4 Pryconsa project
Madrileña Red de Gas continues to make progress in the production and supply of green hydrogen for homes. In 2023, in collaboration with the company ARUP, the conceptual study of the hydrogen storage solution was conducted for a 100-home development in the municipality of Valdemoro. The technical constraints and the limitations of the available space have reduced the feasibility of this solution, so it has been decided to study the on-site production of hydrogen, channelling it from the outdoor plot to the development’s central boiler.
It becomes clear that producing hydrogen on a small, local scale would not be competitive, and would increase the cost for the end user. However, an optimal alternative exists that will be developed through the use of “Ready for H2” boilers, which are starting to become available on the market, fully capable of both using existing natural gas infrastructures and running on hydrogen in the future with minimal adaptations, enabling hydrogen to reach all current consumption points. As part of this initiative, the central boiler will be a Bosch model that can work with hydrogen, natural gas and biomethane, making it the first installation in Madrid capable of working with any of these renewable fuels.
Construction of the housing development is scheduled to begin in early 2024. The engineering project is currently being finalised.
For more information: https://madrilena.es/ponemos-en-marcha-el-primer-proyecto-con-produccion-y-suministro-de-hidrogeno-verde-para-viviendas/
5.5 Cavendish and Heat Pump Studies (ADL)
In 2023, Asociación Española del Gas (Spanish Gas Association) in collaboration with the other distributors, was working on different studies on the viability of hydrogen and biomethane in the gas network and its comparison with electric heat pumps.
The Cavendish study concluded that renewable gases will be competitive in all consumption segments from 2030, and will play a key role in the energy transition in the transport and power generation sector, strengthening their position as the best option from 2040 onwards
Cavendish study
The first of these studies is Cavendish, carried out with the consultancy firm BIP, analysing the competitiveness and viability of renewable gases.
The Cavendish study concluded that renewable gases will be competitive in all consumption segments from 2030, and will play a key role in the energy transition in the transport and power generation sector, strengthening their position as the best option from 2040 onwards.
It is clear that most infrastructures could run on up to 20% hydrogen without major adaptation efforts, whereas a pure hydrogen scenario will require higher investment. In terms of material compatibility, the study carried out, using a probabilistic model, indicates that more than 97% of the grid would be suitable for hydrogen operation.
Considering these costs, the CavendisH2 scenario proposes an alternative to the high electrification scenario: the annual investment required would be 22% lower, mainly due to a lower marginal cost of grid reinforcement and retrofitting of residential equipment. The scenario with a higher penetration of renewable gases would imply less effort in terms of costs.
For more information: https://madrilena.es/ya-podriamos-estar-usando-un-20-de-hidrogeno-renovable-la-red-de-gas-espanola-funcionaria-con-una-inversion-minima-para-su-adecuacion/
Heat pump study
Conducted together with Arthur D. Little, this study focuses on heat pumps and the competitiveness of natural gas boilers that use this system. The main conclusions drawn are as follows:
- Condensing boilers fuelled by renewable gases are a solution that makes it possible to achieve the net zero targets for the building industry in Spain for 2030 and 2050.
- It is not the type of equipment, boiler or heat pump that makes a technological solution “green”, but rather the fuel it uses. Boilers are both efficient and affordable, and their renewable nature depends on the fuel they use.
- Given the type of building and considering the population’s average purchasing power, achieving net zero by heat pump will not be possible in Spain. The investment required to implement heat pump systems can exceed 90% of the average annual income of Madrid households.
- Replacing atmospheric boilers with condensing boilers, combined with developing the potential of renewable gases in Spain, is now the most economically efficient alternative for achieving net zero in Spanish households, and the one most likely to succeed.
For more information:
- https://madrilena.es/bomba-de-calor-limitaciones-de-espacio-en-las-viviendas/
- https://madrilena.es/el-desafio-de-la-eficiencia-energetica-tener-18-000-euros-no-es-la-solucion/
5.6 Biomethane
Throughout 2023, Madrileña Red de Gas received several formal requests to connect biomethane plants to its distribution network. One formal application has already been made and two are in the pipeline.
- Project East Madrid: this is the most advanced project in biogas production. Injection of biomethane into the grid is planned for December 2025.
- Two projects in the south of Madrid: these are in the processing phase, pending the official application for connection to the distribution network. Biomethane injections are planned for 2026.
